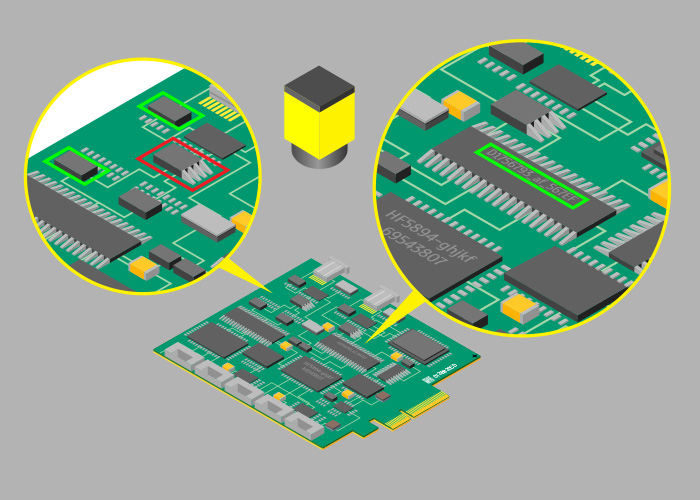
1. The weldability of the plate hole affects the welding quality
The poor solderability of the circuit board holes will result in PCB Assembly and welding defects, which will affect the parameters of the components in the circuit, leading to unstable conduction between the components of the multilayer board and the inner line, causing the failure of the entire circuit. The so-called solderability refers to the property that the metal surface is wetted by molten solder, that is, a relatively uniform continuous smooth adhesion film is formed on the metal surface of the solder.

The main factors affecting the solderability of printed circuit boards:
(1) The composition of the solder and the properties of the solder.
Solder is a vital part of the welding chemical treatment process. It consists of chemical substances containing flux. Commonly used low melting point eutectic metals are Sn-Pb or Sn-Pb-ag. The impurity content should be controlled in a certain proportion. To prevent the oxides generated by impurities from being dissolved by the flux. The function of the flux is to help the solder to wet the surface of the soldered board by transferring heat and removing rust. White rosin and isopropanol solvents are generally used.
(2) The welding temperature and the cleanliness of the metal plate surface also affect the weldability.
When the temperature is too high, the solder spreading speed increases. At this time, the activity is high, the circuit board and the solder melting surface are rapidly oxidized, causing solder defects, and the surface of the circuit board is contaminated, which also affects the solderability and causes defects. Including tin beads, tin balls, disconnection, poor gloss, etc.
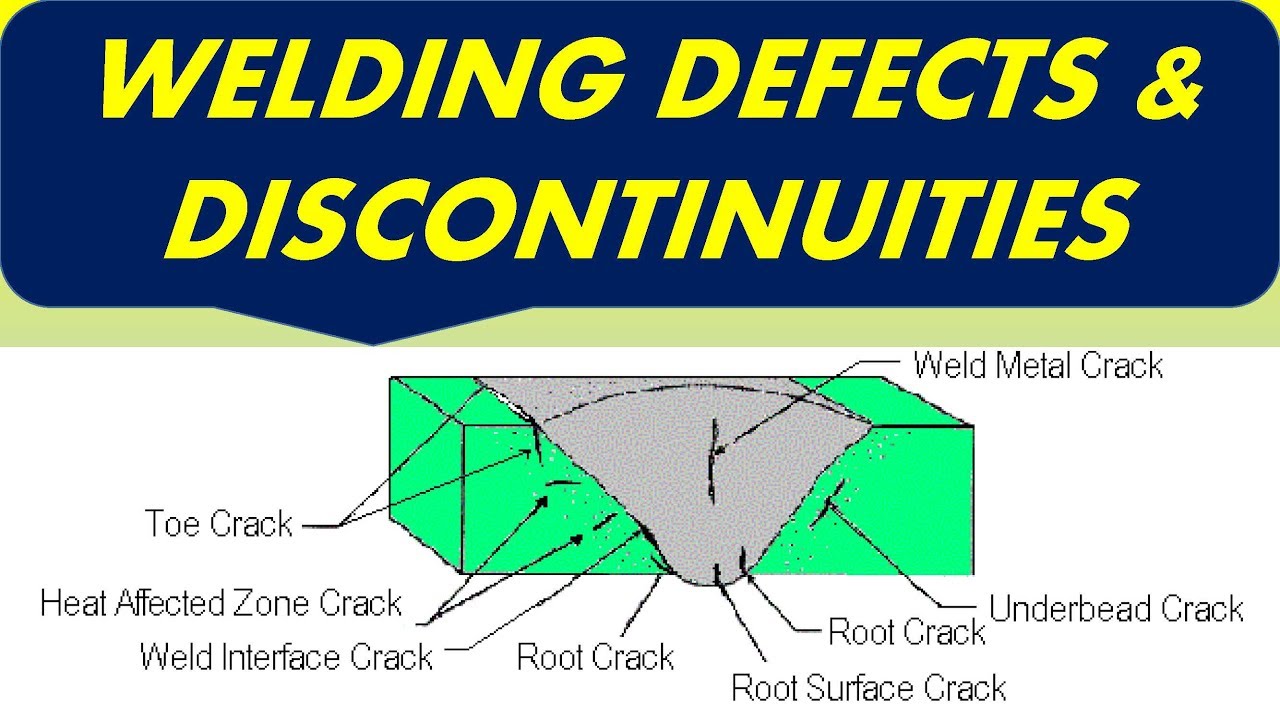
2. PCBA welding defects caused by warpage
Circuit boards and components warp during welding, and stress deformation causes PCBA processing welding defects such as solder joints and short circuits. Warpage is often caused by temperature imbalance between the upper and lower parts of the board. For large PCBs, warpage may occur due to the weight of the board itself. Ordinary PBGA devices are about 0.5mm away from the printed circuit board. If the equipment on the circuit board is large, the circuit board will return to its normal shape after cooling, and the solder joints will be stressed for a long time.
3. PCB design affects welding quality
In PCB layout, when the size of the circuit board is too large, although the soldering is easier to control, but the printed line is long, the impedance increases, the noise resistance decreases, and the cost increases; If the temperature is too small, the heat dissipation decreases, the soldering is difficult to control, and it is easy to be adjacent line. Mutual interference, such as electromagnetic interference to the board.
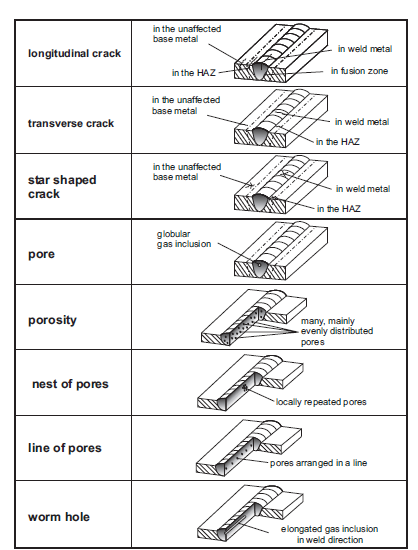
Therefore, PCB design must be optimized:
(1) Shorten the wiring between high-frequency components to reduce electromagnetic interference.
(2) Components with heavier weight (such as 20g or more) are fixed with brackets and then welded.
(3) The heat dissipation problem should be considered for heating elements to prevent large defects and rework on the surface of the elements, and the thermal elements should be kept away from heat sources.
(4) The arrangement of the components is as parallel as possible, which is beautiful and easy to weld, and should be mass-produced. The board is designed as the best 4:3 rectangle. Do not change the line width to avoid intermittent wiring. When the board is heated for a long time, the copper foil is easy to expand and fall off, so avoid large area copper foil.